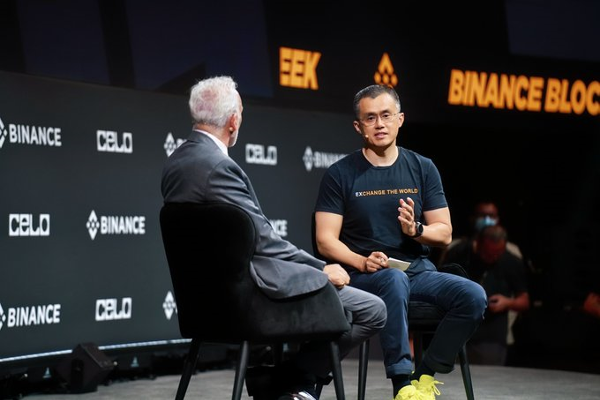
Ethereum Foundation dAI Team and ConsenSys Launch ERC-8004 Protocol to Bootstrap AI Agent Economy

As reported, the Ethereum Foundation's DAI team and ConsenSys today announced the final version of ERC-8004, a protocol that allows artificial intelligence agents to discover, verify, and collaborate with each other without a centralized intermediary. This development bridges the gap between blockchain and AI.
Drafted in August of this year, ERC-8004 addresses this problem through three lightweight on-chain registries: identity, reputation, and verification. Since its launch, ERC-8004 has fostered numerous working prototypes and generated widespread interest, with over one hundred companies planning to build on top of the protocol. The final specification, announced today, was signed by Marco De Rossi (MetaMask), Davide Crapis (Ethereum Foundation), Jordan Ellis (Google), and Erik Reppel (Coinbase), and incorporates extensive community feedback, including contributions from Cisco, EigenLayer, Eliza Labs, ENS, Nethermind, OpenZeppelin, Phala, The Graph, and Virtuals.
ERC-8004 assigns each agent a portable on-chain identity as an ERC-721 token. This means agents are tokenized as NFTs and can be minted, viewed in wallets, transferred, and managed (including licensing to operators) using existing ERC-721 applications. This token points to a standards-based registration file that describes the agent's name, skills, and public endpoints (including A2A, MCP, ENS/did, and wallets). Because this description adheres to open standards on a neutral infrastructure, it can be indexed by any browser or marketplace, enabling permissionless discovery across providers and platforms.
In addition to identity and discovery, ERC-8004 also enables on-chain reputation: clients and agents can submit structured feedback with tags, such as by skill or task, and, where relevant, attach x402 proof of payment, to reinforce trustworthiness in economic interactions.